Deep Learning - CNN - Convolutional Neural Network - Backpropagation in CNN Tutorial
What is BackPropagation?
It is an algorithm to train neural networks. It is the method of fine-tuning the weights of a neural network based on the error rate obtained in the previous epoch (i.e., iteration).
Backpropagation, short for "backward propagation of errors," is an algorithm for supervised learning of artificial neural networks using gradient descent. Given an artificial neural network and an error function, the method calculates the gradient of the error function with respect to the neural network's weights using the chain rule.
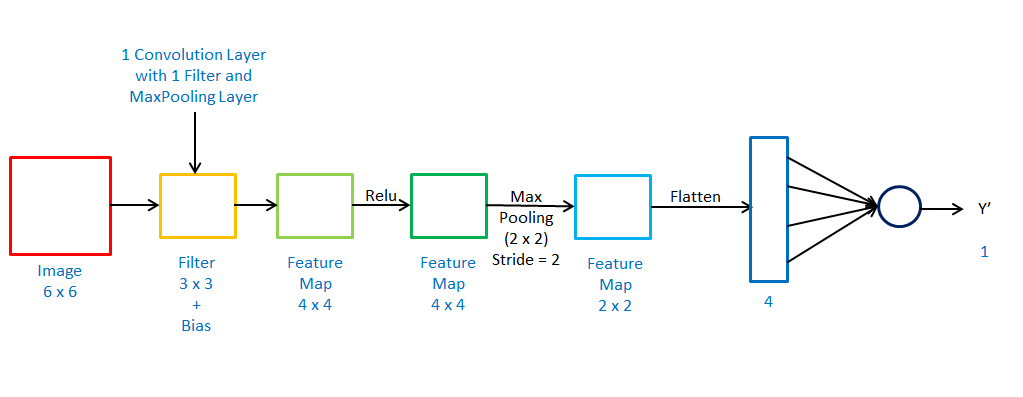
Total Trainable Parameters-
W1 = (3,3) and W2 = (1,4)
b1 = (1,1) and b2 = (1,1)
is equal to 15 trainable parameter
Loss for Binary Classification is
L = -Yi log(Y'i) - (1 - Yi) log(1 - Y'i)
Forward Propagation-
Z1 = Conv(X, W1) + b1
A1 = Relu(Z1)
P1 = MaxPool(A1)
F = Flatten(P1)
Z2 = FW2 + b2
A2 = \(\sigma\)(Z2)
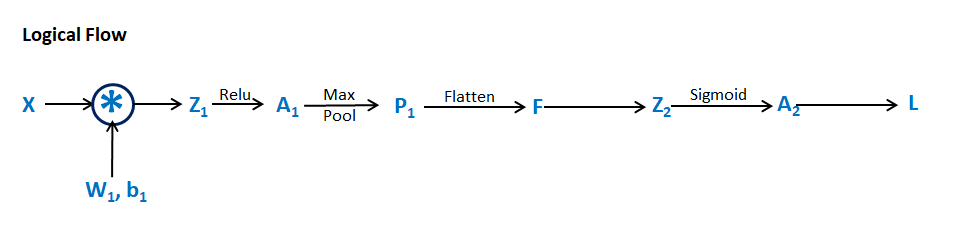
Backward Propagation-
we have to apply a gradient descent algorithm on all trainable parameters till the loss is minimized
\(W_{1} = W_{1} - \eta\frac{\delta L}{\delta W_{1}}\)
\(b_{1} = b_{1} - \eta\frac{\delta L}{\delta b_{1}}\)
\(W_{2} = W_{2} - \eta\frac{\delta L}{\delta W_{2}}\)
\(b_{2} = b_{2} - \eta\frac{\delta L}{\delta b_{2}}\)
Finding the derivative-
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta W_{2}} = \frac{\delta L}{\delta A_2} \times \frac{\delta A_2}{\delta Z_{2}}\times \frac{\delta Z_{2}}{\delta W_{2}}\)
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta b_{2}} = \frac{\delta L}{\delta A_2} \times \frac{\delta A_2}{\delta Z_{2}}\times \frac{\delta Z_{2}}{\delta b_{2}}\)
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta W_{1}} = \frac{\delta L}{\delta A_2} \times \frac{\delta A_2}{\delta Z_{2}}\times \frac{\delta Z_{2}}{\delta F}\times \frac{\delta F}{\delta P_1}\times \frac{\delta P_1}{\delta A_1}\times \frac{\delta A_1}{\delta Z_1}\times \frac{\delta Z_1}{\delta W_1}\)
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta b_{1}} = \frac{\delta L}{\delta A_2} \times \frac{\delta A_2}{\delta Z_{2}}\times \frac{\delta Z_{2}}{\delta F}\times \frac{\delta F}{\delta P_1}\times \frac{\delta P_1}{\delta A_1}\times \frac{\delta A_1}{\delta Z_1}\times \frac{\delta Z_1}{\delta b_1}\)
Denoting A2 Matrix as a2 single image
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta a_{2}} \) =\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta a_2} [-Y_i log(a_2) - (1 - Y_i) log(1 - a_2)]\)
= \(-\frac{Y_i}{\delta a_{2}} + \frac{(1 - Y_i)}{(1 - a_2)}=\frac{-Y_i(1 - a_2) + a_2(1-Y_i)}{a_2(1 - a_2)}\) =\(\frac{-Y_i + Y_i a_2 + a_2 - a_2 Y_i}{a_2(1 - a_2)}\)
=\(\frac{(a_2 - Y_i)}{a_2(1-a_2)}\)
\(\frac{\delta A_2}{\delta Z_{2}} \) =\(\sigma(Z_2)[1 - \sigma(Z_2)]\) = a2[1 - a2]
\(\frac{\delta Z_2}{\delta W_{2}} \) = F
\(\frac{\delta Z_2}{\delta b_{2}} \) = 1
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta W_{2}} \) = \(\frac{(a_2 - Y_i)}{a_2(1-a_2)}\times a_2(1 - a_2) \times F\) = \((a_2 -Y_i)F^T\) = \((A_2 -Y)F^T\)
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta b_{2}} \)= \(\frac{(a_2 - Y_i)}{a_2(1-a_2)}\times a_2(1 - a_2) \times 1\) = \((a_2 -Y_i)\) = \((A_2 -Y)\)
\(\frac{\delta Z_2}{\delta F} \) = W2
\(\frac{\delta F}{\delta P_{1}} \) = reshape(P1.shape)
\(\frac{\delta L}{\delta A_1}= \begin{cases} \frac{\delta L}{\delta P_{1xy}} & \quad \text{,if } A_{mn} \text{ is the max element}\\ 0 & \quad \text{,otherwise} \end{cases} \)
\(\frac{\delta A_1}{\delta Z_1}= \begin{cases} 1 & \quad \text{,if } Z_{1xy} \text{ > 0}\\ 0 & \quad \text{,if } Z_{1xy} \text{ < 0}\\ \end{cases} \)