Python - Decision control and looping statement - if-else Tutorial
Python if…else is a decision-making statement that is used to check whether the condition is True Or False.
If the first condition in if block is false it will check the next condition in elif block. If the elif block condition is also false then it will finally execute else block.
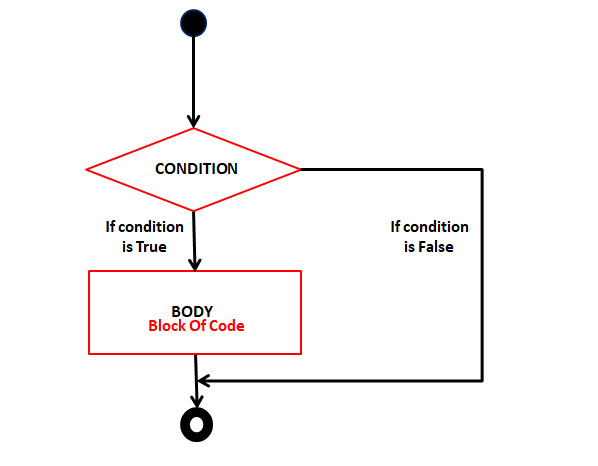
- If statement
It executes if block only when if condition is true.
a = 2
b = 7
if a > b:
print("a is greater than b")
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
Output-
b is greater than a
In shorthand, it can also be written as
a = 9
b = 7
if a > b: print("a is greater than b")
Output-
a is greater than b
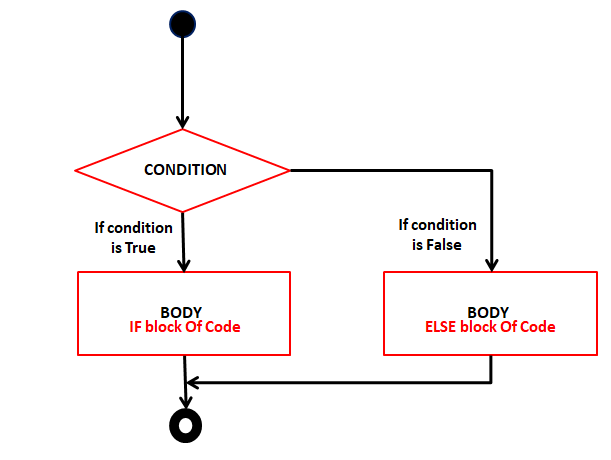
- If-else statement
It checks first for if condition, if the condition is true, it will execute if block, otherwise it will execute else block.
a = 2
b = 7
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
else:
print("a is greater than b")
Output-
b is greater than a
In shorthand, it can also be written as
a = 9
b = 7
print("a is greater than b") if(a>b) else print("b is greater than a")
Output-
a is greater than b
It is also known as the ternary operator.
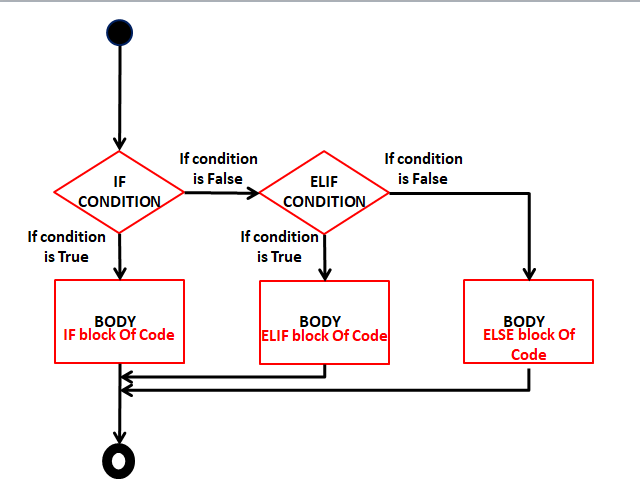
- If-elif-else ladder
It checks first for if condition, if the condition is true, it will execute if block, otherwise it will go to next condition i.e elif.
If the condition went false, it will again move toward the next elif condition, still, the condition becomes true.
At last, if no condition is satisfied, finally it will execute else block.
a = 9
b = 7
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
elif a == b:
print("a is equal to b")
else:
print("a is greater than b")
Output-
a is greater than b
- Nested If else
One if-else condition nested under another if-else condition is known as nested if else. If the outer condition is true, then it will execute the inner condition only when it become true.
a = 9
b = 7
c = 3
if(a>b):
if(a>c):
print("a is greater")
else:
print("c is greater")
else:
if(b>c):
print("b is greater")
else:
print("c is greater")
Output-
a is greater