Python - Things to know before proceed - Ascii, Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal Tutorial
ASCII
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
It a numeric value given to each character and symbol, which is used as a standard data-encoding format for electronic communication between computers.
We can find ASCII value of char using ord().
Program to find ASCII Value of any character-
char = 'A'
print("The ASCII value of '" + char + "' is", ord(char))Output-
65
ASCII Table
|
Decimal |
Hexadecimal |
Binary |
Char |
Description |
|
0 |
00 |
00000000 |
NUL |
Null |
|
1 |
01 |
00000001 |
SOH |
Start of Header |
|
2 |
02 |
00000010 |
STX |
Start of Text |
|
3 |
03 |
00000011 |
ETX |
End of Text |
|
4 |
04 |
00000100 |
EOT |
End of Transmission |
|
5 |
05 |
00000101 |
ENQ |
Enquiry |
|
6 |
06 |
00000110 |
ACK |
Acknowledge |
|
7 |
07 |
00000111 |
BEL |
Bell |
|
8 |
08 |
00001000 |
BS |
Backspace |
|
9 |
09 |
00001001 |
HT |
Horizontal Tab |
|
10 |
0A |
00001010 |
LF |
Line Feed |
|
11 |
0B |
00001011 |
VT |
Vertical Tab |
|
12 |
0C |
00001100 |
FF |
Form Feed |
|
13 |
0D |
00001101 |
CR |
Carriage Return |
|
14 |
0E |
00001110 |
SO |
Shift Out |
|
15 |
0F |
00001111 |
SI |
Shift In |
|
16 |
10 |
00010000 |
DLE |
Data Link Escape |
|
17 |
11 |
00010001 |
DC1 |
Device Control 1 |
|
18 |
12 |
00010010 |
DC2 |
Device Control 2 |
|
19 |
13 |
00010011 |
DC3 |
Device Control 3 |
|
20 |
14 |
00010100 |
DC4 |
Device Control 4 |
|
21 |
15 |
00010101 |
NAK |
Negative Acknowledge |
|
22 |
16 |
00010110 |
SYN |
Synchronize |
|
23 |
17 |
00010111 |
ETB |
End of Transmission Block |
|
24 |
18 |
00011000 |
CAN |
Cancel |
|
25 |
19 |
00011001 |
EM |
End of Medium |
|
26 |
1A |
00011010 |
SUB |
Substitute |
|
27 |
1B |
00011011 |
ESC |
Escape |
|
28 |
1C |
00011100 |
FS |
File Separator |
|
29 |
1D |
00011101 |
GS |
Group Separator |
|
30 |
1E |
00011110 |
RS |
Record Separator |
|
31 |
1F |
00011111 |
US |
Unit Separator |
|
32 |
20 |
00100000 |
space |
Space |
|
33 |
21 |
00100001 |
! |
exclamation mark |
|
34 |
22 |
00100010 |
" |
double quote |
|
35 |
23 |
00100011 |
# |
number |
|
36 |
24 |
00100100 |
$ |
dollar |
|
37 |
25 |
00100101 |
% |
percent |
|
38 |
26 |
00100110 |
& |
ampersand |
|
39 |
27 |
00100111 |
' |
single quote |
|
40 |
28 |
00101000 |
( |
left parenthesis |
|
41 |
29 |
00101001 |
) |
right parenthesis |
|
42 |
2A |
00101010 |
* |
asterisk |
|
43 |
2B |
00101011 |
+ |
plus |
|
44 |
2C |
00101100 |
, |
comma |
|
45 |
2D |
00101101 |
- |
minus |
|
46 |
2E |
00101110 |
. |
period |
|
47 |
2F |
00101111 |
/ |
slash |
|
48 |
30 |
00110000 |
0 |
zero |
|
49 |
31 |
00110001 |
1 |
one |
|
50 |
32 |
00110010 |
2 |
two |
|
51 |
33 |
00110011 |
3 |
three |
|
52 |
34 |
00110100 |
4 |
four |
|
53 |
35 |
00110101 |
5 |
five |
|
54 |
36 |
00110110 |
6 |
six |
|
55 |
37 |
00110111 |
7 |
seven |
|
56 |
38 |
00111000 |
8 |
eight |
|
57 |
39 |
00111001 |
9 |
nine |
|
58 |
3A |
00111010 |
: |
colon |
|
59 |
3B |
00111011 |
; |
semicolon |
|
60 |
3C |
00111100 |
< |
less than |
|
61 |
3D |
00111101 |
= |
equality sign |
|
62 |
3E |
00111110 |
> |
greater than |
|
63 |
3F |
00111111 |
? |
question mark |
|
64 |
40 |
01000000 |
@ |
at sign |
|
65 |
41 |
01000001 |
A |
|
|
66 |
42 |
01000010 |
B |
|
|
67 |
43 |
01000011 |
C |
|
|
68 |
44 |
01000100 |
D |
|
|
69 |
45 |
01000101 |
E |
|
|
70 |
46 |
01000110 |
F |
|
|
71 |
47 |
01000111 |
G |
|
|
72 |
48 |
01001000 |
H |
|
|
73 |
49 |
01001001 |
I |
|
|
74 |
4A |
01001010 |
J |
|
|
75 |
4B |
01001011 |
K |
|
|
76 |
4C |
01001100 |
L |
|
|
77 |
4D |
01001101 |
M |
|
|
78 |
4E |
01001110 |
N |
|
|
79 |
4F |
01001111 |
O |
|
|
80 |
50 |
01010000 |
P |
|
|
81 |
51 |
01010001 |
Q |
|
|
82 |
52 |
01010010 |
R |
|
|
83 |
53 |
01010011 |
S |
|
|
84 |
54 |
01010100 |
T |
|
|
85 |
55 |
01010101 |
U |
|
|
86 |
56 |
01010110 |
V |
|
|
87 |
57 |
01010111 |
W |
|
|
88 |
58 |
01011000 |
X |
|
|
89 |
59 |
01011001 |
Y |
|
|
90 |
5A |
01011010 |
Z |
|
|
91 |
5B |
01011011 |
[ |
left square bracket |
|
92 |
5C |
01011100 |
\ |
backslash |
|
93 |
5D |
01011101 |
] |
right square bracket |
|
94 |
5E |
01011110 |
^ |
caret / circumflex |
|
95 |
5F |
01011111 |
_ |
underscore |
|
96 |
60 |
01100000 |
` |
grave / accent |
|
97 |
61 |
01100001 |
a |
|
|
98 |
62 |
01100010 |
b |
|
|
99 |
63 |
01100011 |
c |
|
|
100 |
64 |
01100100 |
d |
|
|
101 |
65 |
01100101 |
e |
|
|
102 |
66 |
01100110 |
f |
|
|
103 |
67 |
01100111 |
g |
|
|
104 |
68 |
01101000 |
h |
|
|
105 |
69 |
01101001 |
i |
|
|
106 |
6A |
01101010 |
j |
|
|
107 |
6B |
01101011 |
k |
|
|
108 |
6C |
01101100 |
l |
|
|
109 |
6D |
01101101 |
m |
|
|
110 |
6E |
01101110 |
n |
|
|
111 |
6F |
01101111 |
o |
|
|
112 |
70 |
01110000 |
p |
|
|
113 |
71 |
01110001 |
q |
|
|
114 |
72 |
01110010 |
r |
|
|
115 |
73 |
01110011 |
s |
|
|
116 |
74 |
01110100 |
t |
|
|
117 |
75 |
01110101 |
u |
|
|
118 |
76 |
01110110 |
v |
|
|
119 |
77 |
01110111 |
w |
|
|
120 |
78 |
01111000 |
x |
|
|
121 |
79 |
01111001 |
y |
|
|
122 |
7A |
01111010 |
z |
|
|
123 |
7B |
01111011 |
{ |
left curly bracket |
|
124 |
7C |
01111100 |
| |
vertical bar |
|
125 |
7D |
01111101 |
} |
right curly bracket |
|
126 |
7E |
01111110 |
~ |
tilde |
|
127 |
7F |
01111111 |
DEL |
delete |
Binary Value
Binary Value are represented by base 2. there are only two symbol used to represent the binary value, i.e 0 and 1.
Binary Number = 1101011
Decimal value = (1*(2^6)) + (1*(2^5)) + (0*(2^4)) +
(1*(2^3)) + (0*(2^2)) + (1*(2^1)) +
(1*(2^0))
= 107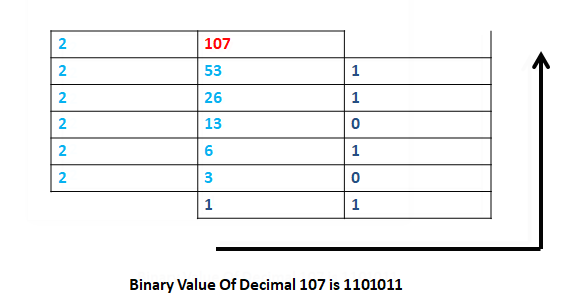
In Python, you can simply use the bin() function to convert from a decimal value to its corresponding binary value.
print(bin(107))
print(bin(22))
print(bin(90))Output-
0b1101011
0b10110
0b1011010
Similarly, int(),oct(),hex() is used to convert from a binary value to its corresponding decimal, octal and hexadecimal value respectively.
print(int(0b1101011)) #OR print(int('1101011',2)) #base2
print(oct(0b1101011))
print(hex(0b1101011))Output-
107
0o153
0x6bOctal Value
Octal Value are represented by base 8. there are represented by only 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
Octal Number = 458
Decimal value = (4*(8^2)) + (5*(8^1)) + (8*(8^0))
= 712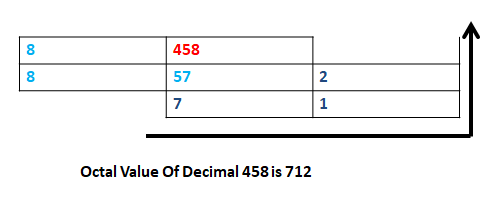
In Python, you can simply use the oct() function to convert from a decimal value to its corresponding octal value.
print(oct(107))
print(oct(22))
print(oct(90))Output-
0o153
0o26
0o132
Similarly, int(),hex(),bin() is used to convert from a octal value to its corresponding decimal, hexadecimal and binary value respectively.
print(int(0o153)) #OR print(int('153',8)) #base8
print(hex(0o153))
print(bin(0o153))Output-
107
0x6b
0b1101011Hexadecimal Value
Hexadecimal Values are represented by base 16. there are represented by only 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
Hexadecimal Number = 7F
Decimal value = (7*(16^1)) + (16*(16^0))
= 127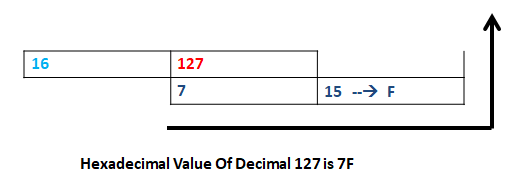
In Python, you can simply use the hex() function to convert from a decimal value to its corresponding hexadecimal value.
print(hex(107))
print(hex(22))
print(hex(90))Output-
0x6b
0x16
0x5a
Similarly, int(),bin(),oct() is used to convert from a hexadecimal value to its corresponding decimal, binary and octal value respectively.
print(int(0x7F)) #OR print(int('7F',16)) #base16
print(hex(0x7F))
print(bin(0x7F))Output-
127
0x7f
0b1111111